What is Mammalian Cell Banking and Why Does It Matter?
Mammalian cell banking is a critical process in biotechnology, especially in the development of biopharmaceuticals. It involves creating a cell bank of mammalian cells, which are stored and used as the starting point for producing biologic drugs. The cells are genetically engineered to produce therapeutic proteins or antibodies, and their ability to replicate and produce these proteins over an extended period makes them invaluable in drug discovery and development.
The importance of mammalian cell banking is growing, especially with the increasing demand for monoclonal antibodies, gene therapies, and biosimilars. As biopharmaceutical companies develop more complex treatments, the need for reliable and reproducible cell banks has never been higher. These cell lines serve as the foundation for drug production, ensuring that the therapies produced are both safe and effective.
How Mammalian Cell Banking Supports Biopharmaceuticals
Mammalian cells, particularly Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, are the preferred choice for the production of biologic drugs. Unlike bacterial or yeast cells, mammalian cells are capable of post-translational modifications, such as glycosylation, which are critical for ensuring that therapeutic proteins are active and functional in the human body.
The process of cell banking ensures that these cells can be preserved over time, maintaining their ability to replicate and produce proteins consistently. This is essential for large-scale drug production, as it ensures that the same batch of cells can be used to produce the drug over many years without significant changes in quality or efficacy.
Mammalian Cell Banks and Their Role in Drug Development
In drug development, mammalian cell banks play an essential role in the following areas:
- Production of Biologics: The cells are used to create large quantities of therapeutic proteins that can be used to treat a wide variety of diseases, from cancer to autoimmune disorders.
- Quality Control: Cell banks are integral in ensuring that the proteins produced meet the required standards of purity, potency, and safety. By using cell lines from a standardized, well-characterized cell bank, companies can maintain consistency across batches.
- Cost Efficiency: Mammalian cell banks reduce the need to create new cell lines for each drug development project. Instead, existing, well-characterized cell lines are used, which lowers production costs and speeds up the development timeline.
Why Are Mammalian Cell Banks So Crucial for Biotech Innovation?
Mammalian cell banking is a key component of the biotech ecosystem. As the demand for biologic drugs continues to rise, the role of cell banks is becoming more significant in the production of therapeutic proteins, vaccines, and gene therapies. Here’s how mammalian cell banks are driving innovation in the biotech industry:
- Enabling Personalized Medicine: The flexibility and scalability of mammalian cells make them ideal for developing personalized therapies. With the right genetic modifications, cell banks can be used to produce customized drugs tailored to individual patient profiles, especially in the field of gene therapies.
- Supporting Biosimilars: The growth of the biosimilars market—the production of generic versions of biologic drugs—relies heavily on mammalian cell banking. By developing standardized cell banks, companies can replicate the production of complex proteins found in originator biologics, creating high-quality and cost-effective alternatives.
- Advancing Gene Therapy: Gene therapies aim to treat or cure genetic disorders by introducing new or modified genes into a patient's cells. Mammalian cell banking plays a crucial role in this process by providing a reliable source of cells that can be engineered to produce the therapeutic genes required for treatment.
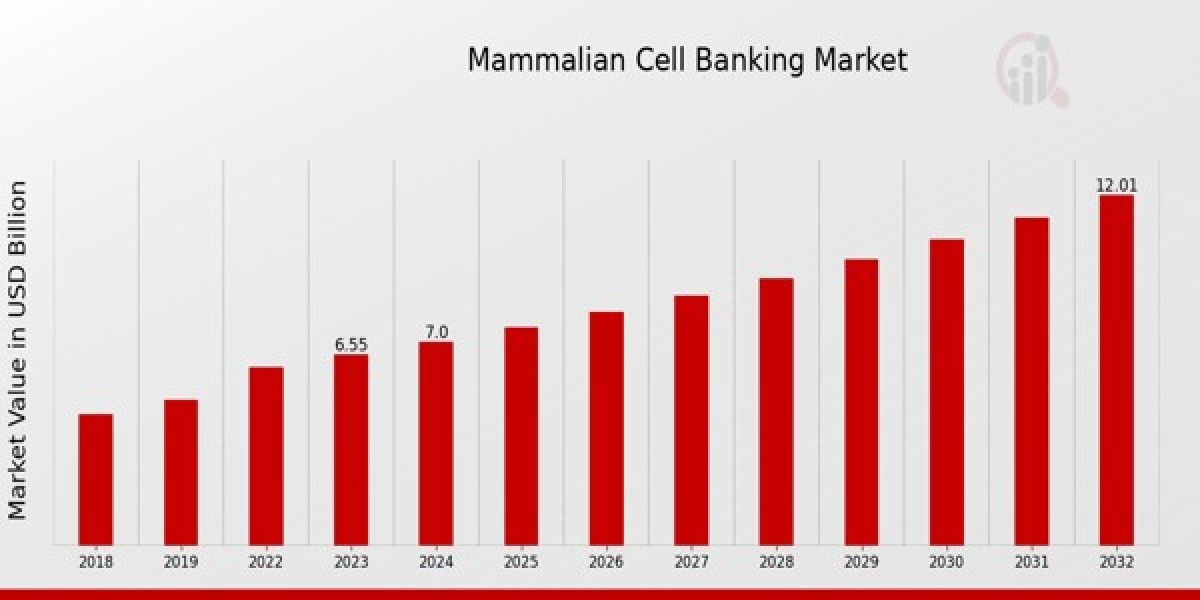
Mammalian Cell Banking Market Overview
As per MRFR analysis, the Mammalian Cell Banking Market Size was estimated at 7.49 (USD Billion) in 2024. The Mammalian Cell Banking Market Industry is expected to grow from 8.01 (USD Billion) in 2025 to 14.70 (USD Billion) till 2034, at a CAGR (growth rate) is expected to be around 6.97% during the forecast period (2025 - 2034).
The Future of Mammalian Cell Banking
As the biopharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, so too does the role of mammalian cell banking. The increasing complexity of biologic drugs, combined with the rising demand for personalized medicine, is pushing the boundaries of what these cell lines can do.
Here are a few trends shaping the future of mammalian cell banking:
- Automation and Advanced Technologies: The integration of automation and advanced bioprocessing techniques is helping streamline cell banking processes, improving efficiency and scalability. These innovations ensure that mammalian cell banks can support the large-scale production of biologic drugs.
- Improved Cell Line Development: Researchers are constantly working to improve the quality and consistency of cell lines. New methods of genetic engineering and cell culture are enabling the creation of more robust and efficient cell lines that can produce higher yields of therapeutic proteins.
- Regulatory Advancements: As the demand for biologics and biosimilars grows, regulatory bodies are evolving their guidelines for mammalian cell banking to ensure that the produced therapies meet stringent safety and quality standards. Companies are investing in regulatory compliance to streamline the approval process and ensure their products meet global standards.
Challenges in the Mammalian Cell Banking Market
While the mammalian cell banking market offers significant opportunities, there are also challenges that companies must navigate:
- Cell Line Characterization: Ensuring that the cells used in the bank are stable and consistent over time is critical. The cells need to maintain their ability to produce therapeutic proteins at the same quality and quantity throughout their lifespan.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The highly regulated nature of the biopharmaceutical industry means that mammalian cell banks must meet strict standards to ensure that the resulting drugs are safe for human use. Adhering to evolving regulations is a key challenge for companies in the market.
- Storage and Handling: Proper storage and handling of cell banks are vital to maintaining cell line integrity. Advances in cryopreservation techniques and biobank management are helping address these challenges, ensuring that cell banks can be stored for extended periods without loss of function.
Conclusion: A Bright Future for Mammalian Cell Banking
Mammalian cell banking is at the heart of some of the most significant advances in biopharmaceutical development. From monoclonal antibodies to gene therapies, mammalian cell banks are enabling the production of life-saving treatments that would otherwise be impossible to produce. As the demand for biologic drugs continues to rise, so too will the importance of reliable, scalable cell banks.
By advancing the science behind mammalian cell banking, the biotech industry can continue to push the boundaries of innovation, ensuring that patients have access to more effective, personalized, and life-changing treatments.