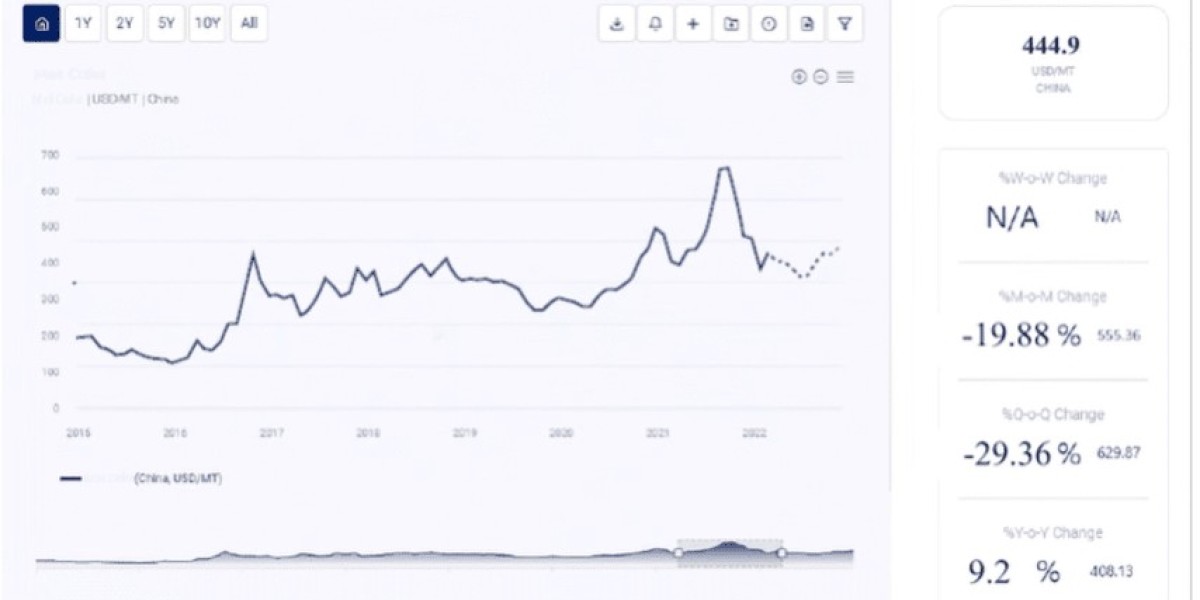
Refined soybean oil is one of the most widely consumed edible oils globally, utilized in a variety of food products and cooking applications. Beyond the kitchen, it’s also used in biofuel production, industrial applications, and even in the cosmetics industry. Due to its broad use and demand, the price trend of refined soybean oil is significant to various industries, consumers, and policymakers. Understanding the factors that influence these price trends is essential for stakeholders to make informed decisions and adapt to market fluctuations.
This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the refined soybean oil price chart, exploring historical data, the factors that influence price changes, and predictions for future trends.
1. Overview of Refined Soybean Oil
1.1 What is Refined Soybean Oil?
Refined soybean oil is derived from the processing of soybeans. After extraction, the crude oil undergoes further refining processes, including degumming, neutralization, bleaching, and deodorization. This refining process removes impurities, free fatty acids, and unwanted substances, resulting in a light-colored oil with a mild flavor suitable for cooking and other uses.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/refined-soybean-oil-price-trends/pricerequest
1.2 Uses of Refined Soybean Oil
The versatility of refined soybean oil makes it a valuable product across various industries:
- Culinary uses: It is commonly used in frying, baking, and salad dressings due to its neutral taste and high smoke point.
- Biofuel: Soybean oil can be converted into biodiesel, providing an alternative renewable energy source.
- Industrial applications: It is used in the manufacturing of soaps, paints, and plastics.
- Cosmetics and personal care: Due to its moisturizing properties, soybean oil is included in various skincare products.
As demand for refined soybean oil spans multiple sectors, price trends can impact several industries simultaneously.
2. Historical Price Trends
Examining the historical price trends of refined soybean oil helps us understand how the market has evolved over time. Refined soybean oil prices have seen fluctuations influenced by various factors, including crop yields, weather patterns, demand for biofuels, and global trade policies.
2.1 Early 2000s to 2010
In the early 2000s, refined soybean oil prices were relatively stable, driven by consistent production and a steady demand from the food industry. However, by the mid-2000s, prices began to climb due to several factors:
- Increased demand for biodiesel: As countries started investing in renewable energy sources, soybean oil became a popular feedstock for biodiesel production, leading to increased demand and higher prices.
- Rising crude oil prices: Since soybean oil is an alternative source for biofuels, its prices often correlate with crude oil prices. The mid-2000s saw a surge in oil prices, which contributed to the rising costs of soybean oil.
By the end of the decade, the economic recession in 2008 caused a temporary decline in prices as demand weakened.
2.2 2011 to 2020
The 2010s saw fluctuations in soybean oil prices due to several global factors:
- Climate and weather impacts: Adverse weather conditions, such as droughts in major soybean-producing countries (the U.S., Brazil, and Argentina), affected crop yields and led to price volatility.
- Trade tensions: Trade disputes between major soybean exporters and importers, particularly between the U.S. and China, had significant impacts on global soybean prices. Tariffs and trade restrictions affected the supply chain and, subsequently, the refined oil market.
- Biofuel mandates: Government policies mandating biofuel use in various countries influenced demand for refined soybean oil as a feedstock, pushing prices upward.
In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic led to a sharp decline in prices as the foodservice sector saw reduced demand. However, the subsequent increase in demand for packaged and processed foods, as well as biofuels, helped prices recover toward the end of the year.
2.3 2021 to Present
Since 2021, refined soybean oil prices have seen a significant surge due to several factors:
- Supply chain disruptions: The pandemic's lingering effects, combined with supply chain challenges, increased production and distribution costs.
- Increased demand for biofuels: Global policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions have spurred a renewed interest in biofuels, leading to a greater demand for soybean oil as a key ingredient.
- Inflation and rising input costs: The cost of fertilizers, labor, and other agricultural inputs has risen, impacting soybean production costs and leading to higher oil prices.
Despite some moderation in prices as supply chains stabilized, refined soybean oil prices have remained relatively high, influenced by ongoing inflationary pressures and changing demand patterns.
3. Factors Influencing Refined Soybean Oil Prices
Several key factors contribute to the fluctuations in refined soybean oil prices, including:
3.1 Crop Yield and Weather Conditions
Soybeans are highly sensitive to weather conditions, with factors like droughts, floods, and frosts directly impacting crop yields. Major soybean-producing countries such as the United States, Brazil, and Argentina often experience volatile weather, which in turn affects the global supply of soybean oil.
3.2 Demand for Biofuels
With increasing efforts to reduce carbon emissions and promote renewable energy sources, the demand for biofuels, including biodiesel, has risen. As soybean oil is a primary feedstock for biodiesel production, any increase in biodiesel demand puts upward pressure on soybean oil prices. Government policies supporting biofuels, such as renewable energy mandates, can significantly impact demand and price.
3.3 Global Trade Policies
Trade relations among major soybean producers and importers, such as the U.S., China, and the EU, play a critical role in setting the market price of soybean oil. Tariffs, quotas, and trade agreements can alter the flow of soybean products across borders, affecting both supply and demand. For instance, trade disputes between the U.S. and China have historically led to price fluctuations due to changes in export and import levels.
3.4 Currency Exchange Rates
As a globally traded commodity, soybean oil prices are affected by currency exchange rates, especially the strength of the U.S. dollar. Since soybean oil is typically priced in dollars, fluctuations in the dollar’s value influence the cost for buyers in other currencies. A stronger dollar generally makes soybean oil more expensive for international buyers, which can reduce demand and lower prices.
3.5 Inflation and Rising Input Costs
In recent years, inflation has increased the costs associated with soybean production, including the prices of fertilizers, pesticides, and labor. Higher production costs are often passed down to consumers, contributing to increased soybean oil prices. Additionally, rising energy costs can affect the refining process, further driving up the price of the final product.
3.6 Consumer Demand in the Food Industry
As an edible oil, soybean oil's demand is closely linked to consumer trends in the food industry. Rising health awareness and dietary trends can impact its popularity. For instance, as plant-based diets become more popular, demand for soybean oil could increase, while concerns over processed foods might temper demand.
4. Future Outlook for Refined Soybean Oil Prices
Several factors are likely to shape the future price trends for refined soybean oil, including:
- Climate change: Continued volatility in weather patterns could result in more frequent disruptions to soybean production, potentially causing price spikes.
- Energy policy shifts: As countries worldwide emphasize renewable energy, demand for biofuels could sustain higher soybean oil prices. Additionally, any change in global energy policies that favors biofuels could further drive up demand.
- Supply chain improvements: As supply chains continue to stabilize following pandemic disruptions, refined soybean oil prices may moderate. However, continued inflation and rising input costs could keep prices elevated.
- Consumer trends: Increasing awareness of sustainable agriculture and plant-based diets could positively influence demand for soybean oil. However, shifts in dietary preferences and health trends may either bolster or reduce consumer demand, affecting prices accordingly.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Leo Frank
Email: sales@procurementresource.com
Toll-Free Number: USA Canada — Phone no: +1 307 363 1045 | UK — Phone no: +44 7537 132103 | Asia-Pacific (APAC) — Phone no: +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA