Cement is a fundamental construction material used globally in the building of infrastructure, residential, commercial, and industrial projects. Understanding the cement price chart is crucial for construction companies, suppliers, developers, and policymakers. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of cement prices, examining the factors influencing these trends, regional variations, and future market forecasts.
Market Overview
Cement is produced by grinding clinker, a mix of limestone and other materials, with gypsum to create a fine powder. The global market for cement is influenced by several factors, including raw material costs, energy costs, production capacities, demand from various construction sectors, and global trade policies.
Current Cement Price Trends
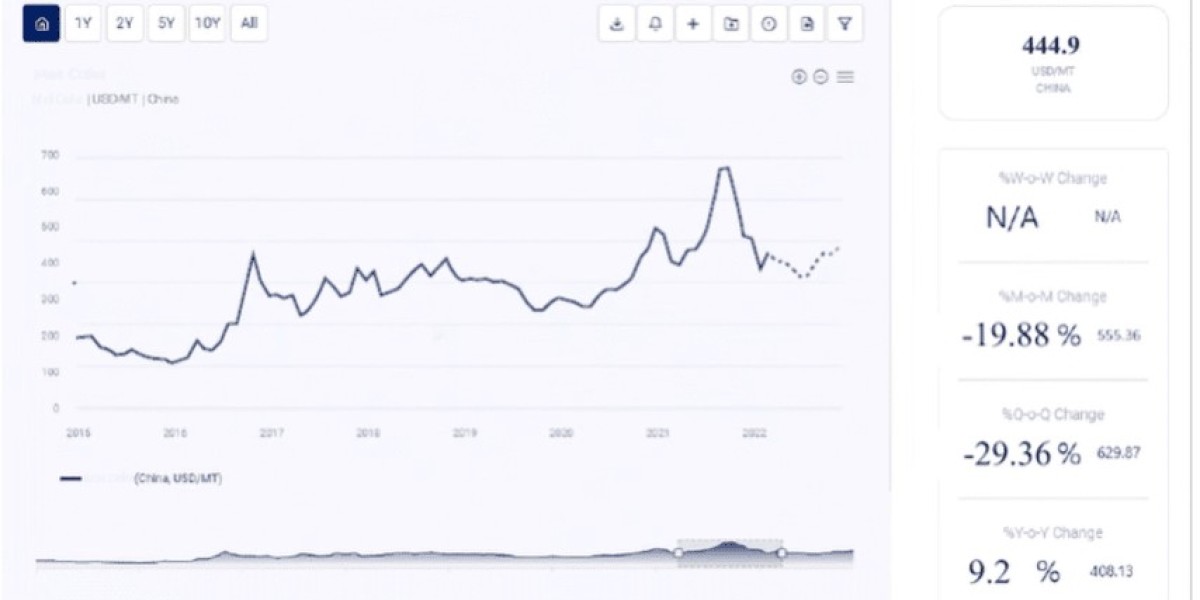
As of mid-2024, cement prices have shown variability due to various market dynamics. The average global price of cement ranges between $90 and $130 per metric ton. Several key factors contribute to these price trends:
Raw Material Costs: The primary raw materials for producing cement are limestone, clay, and gypsum. Fluctuations in the prices of these materials, driven by factors such as mining output, energy costs, and global demand, directly impact production costs.
Energy Costs: The production of cement is energy-intensive, requiring significant amounts of electricity and heat for the kiln operations. Energy costs can vary based on local energy prices and the efficiency of the production process.
Supply and Demand Dynamics: The balance between supply and demand plays a crucial role in determining prices. High demand from the construction and infrastructure sectors and limited supply can drive prices up, while an oversupply can lead to price reductions.
Production Capacities: The global production capacity for cement affects its market price. Expansions in production facilities or the establishment of new plants can lead to a surplus in supply, thereby reducing prices. Conversely, production disruptions can lead to shortages and price hikes.
Global Trade Policies: Trade policies, including tariffs and import/export restrictions, can significantly affect the price of cement. Changes in trade agreements or geopolitical tensions can disrupt supply chains, leading to price volatility.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/cement-price-trends/pricerequest
Regional Price Variations
The price of cement varies across different regions due to local production capacities, demand levels, and regulatory environments. Here is a regional analysis of cement prices:
North America: In the United States and Canada, cement prices range from $100 to $130 per metric ton. Prices are influenced by raw material costs, energy costs, and demand from the construction and infrastructure sectors. The presence of large cement producers in this region also affects pricing dynamics.
Europe: In Europe, the price of cement varies between $90 and $120 per metric ton. The region's stringent environmental regulations and high demand from the construction sector contribute to these prices. Countries like Germany, the UK, and France have significant markets for cement.
Asia-Pacific: The Asia-Pacific region, led by China and India, is a significant market for cement. Prices in this region range from $80 to $110 per metric ton. The growing industrialization and increasing demand for construction materials drive the market. Production costs are generally lower due to less stringent regulations and lower labor costs.
Latin America: In Latin America, the price of cement ranges from $85 to $115 per metric ton. The region's growing construction sector and increasing demand for infrastructure projects are key factors influencing prices. Local production capacities also play a role in determining pricing.
Middle East and Africa: Prices in the Middle East and Africa vary between $90 and $120 per metric ton. The region's developing construction sector and increasing demand for infrastructure projects contribute to the market dynamics. Import dependencies in some countries can also lead to price fluctuations.
Factors Influencing Cement Prices
Several factors play a crucial role in determining the prices of cement:
Raw Material Availability: The availability and price of limestone, clay, and gypsum significantly affect the production cost and price of cement. Disruptions in the supply of these materials can lead to price volatility.
Production Costs: Manufacturing costs, including energy, labor, and maintenance, impact cement prices. Advances in production technology and economies of scale can help reduce costs and stabilize prices.
Demand-Supply Dynamics: The balance between demand and supply in the market influences prices. High demand from the construction and infrastructure sectors and limited supply can drive prices up, while an oversupply can lead to price reductions.
Technological Advancements: Innovations in production processes and the development of new applications for cement can impact its market price. Technological advancements that improve production efficiency or create new market opportunities can influence price trends.
Environmental Regulations: Environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives can impact production processes and costs. Compliance with these regulations may require investments in cleaner technologies, affecting production costs and prices.
Economic Conditions: Global and regional economic conditions influence the demand for construction and infrastructure projects that use cement. Economic downturns can lead to reduced demand and lower prices, while economic growth can drive demand and increase prices.
Applications of Cement
Understanding the diverse applications of cement can provide insights into the factors driving its demand and, consequently, its price. Some of the primary applications include:
Residential Construction: Cement is widely used in the construction of residential buildings, including houses, apartments, and condominiums. The demand from the residential construction sector significantly drives the market.
Commercial Construction: Cement is used in the construction of commercial buildings such as offices, shopping malls, and hotels. The demand from the commercial construction sector impacts the market dynamics.
Infrastructure Projects: Cement is essential for infrastructure projects such as roads, bridges, highways, and airports. The demand from government and private infrastructure projects drives the market.
Industrial Construction: Cement is used in the construction of industrial facilities, including factories, warehouses, and plants. The demand from the industrial construction sector influences the market.
Specialized Construction: Cement is also used in specialized construction applications such as marine structures, dams, and power plants. The demand from these specialized sectors impacts the market dynamics.
Future Price Forecast
The future outlook for cement prices is influenced by various factors, including market demand, raw material costs, technological advancements, and regulatory changes. Here are some key trends and predictions for the future:
Stable Raw Material Prices: If the prices of limestone, clay, and gypsum remain stable, it is likely that the price of cement will also stabilize. However, any significant changes in raw material prices or supply chain disruptions could impact cement prices.
Growing Demand from End-Use Industries: The demand for cement from various construction and infrastructure sectors is expected to continue growing. This increasing demand will likely support price stability or even lead to price increases.
Technological Innovations: Advances in production technology and the development of new applications for cement could drive market growth. Innovations that enhance production efficiency or create new market opportunities may help stabilize or reduce prices.
Environmental and Regulatory Factors: Stricter environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives may impact production processes and costs. Compliance with these regulations could lead to increased production costs, potentially driving prices up.
Economic Recovery: The global economic recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic is expected to boost demand for construction and infrastructure projects that use cement. This increased demand may support higher prices in the short to medium term.
Regional Market Dynamics: Regional differences in production capacity, demand, and regulatory environments will continue to influence cement prices. Markets with strong demand and limited supply may experience higher prices, while regions with surplus production capacity may see more stable or lower prices.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Leo Frank
Email: sales@procurementresource.com
Toll-Free Number: USA & Canada — Phone no: +1 307 363 1045 | UK — Phone no: +44 7537 132103 | Asia-Pacific (APAC) — Phone no: +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA