Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung condition characterized by the permanent dilation and damage of the bronchi, leading to recurrent infections, mucus buildup, and decreased lung function. Despite its increasing prevalence, particularly among older adults, bronchiectasis remains a somewhat under-researched area. This has spurred the need for clinical trials to explore new treatments, improve patient outcomes, and enhance our understanding of the disease. In this article, we delve into the recent clinical trials focused on bronchiectasis, analyzing their findings and implications for future treatment strategies.
The Importance of Clinical Trials in Bronchiectasis
Clinical trials are essential for advancing medical knowledge and developing effective treatments for bronchiectasis. They provide a structured and Bronchiectasis Clinical Trials scientific method to test the safety, efficacy, and side effects of new drugs, therapies, and interventions. With the global burden of bronchiectasis on the rise, clinical trials offer hope for more targeted and effective treatments that can improve the quality of life for patients.
Recent Clinical Trials in Bronchiectasis
- Antibiotic Therapies
- One of the main focuses of bronchiectasis research has been on antibiotic therapies, given the role of bacterial infections in exacerbating the disease. Recent clinical trials have tested the efficacy of long-term antibiotic use in reducing exacerbations. For example, a study involving the antibiotic azithromycin demonstrated a significant reduction in the frequency of exacerbations in patients with non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis. However, concerns about antibiotic resistance and long-term safety remain a challenge that needs further investigation.
- Inhaled Therapies
- Inhaled therapies, including bronchodilators and corticosteroids, have been a mainstay of bronchiectasis management. Recent trials have explored the benefits of inhaled antibiotics like tobramycin and levofloxacin, which are designed to deliver medication directly to the lungs, reducing systemic side effects. These trials have shown promising results in reducing bacterial load and improving lung function, though patient adherence and device optimization continue to be areas for improvement.
- Mucolytic Agents
- The thick mucus associated with bronchiectasis is a significant contributor to disease progression. Clinical trials testing mucolytic agents, such as mannitol and hypertonic saline, have shown that these treatments can help thin mucus, making it easier for patients to clear their airways. These findings suggest that mucolytics could play a crucial role in comprehensive bronchiectasis management.
- Anti-Inflammatory Treatments
- Inflammation is a key component of bronchiectasis pathology. Trials evaluating anti-inflammatory treatments, such as macrolides and statins, have aimed to reduce lung inflammation and slow disease progression. While some studies have shown benefits, others have yielded mixed results, highlighting the need for more research to identify which patients might benefit the most from these therapies.
- Emerging Therapies
- Beyond traditional treatments, there is growing interest in novel therapies, including biologics targeting specific inflammatory pathways and gene therapy approaches aimed at correcting underlying genetic defects. While still in the early stages of research, these innovative therapies hold promise for more personalized and effective treatments in the future.
Challenges and Future Directions
While recent clinical trials have provided valuable insights into bronchiectasis treatment, several challenges remain. These include the heterogeneity of the disease, which makes it difficult to design one-size-fits-all treatments, and the need for long-term studies to fully understand the impact of new therapies. Additionally, the development of biomarkers to identify patients who are most likely to benefit from specific treatments could help to optimize therapy and reduce unnecessary side effects.
Looking forward, the integration of digital health technologies, such as remote monitoring and telemedicine, could enhance patient participation in clinical trials and allow for more comprehensive data collection. These advancements could lead to more precise and effective treatment strategies for bronchiectasis.
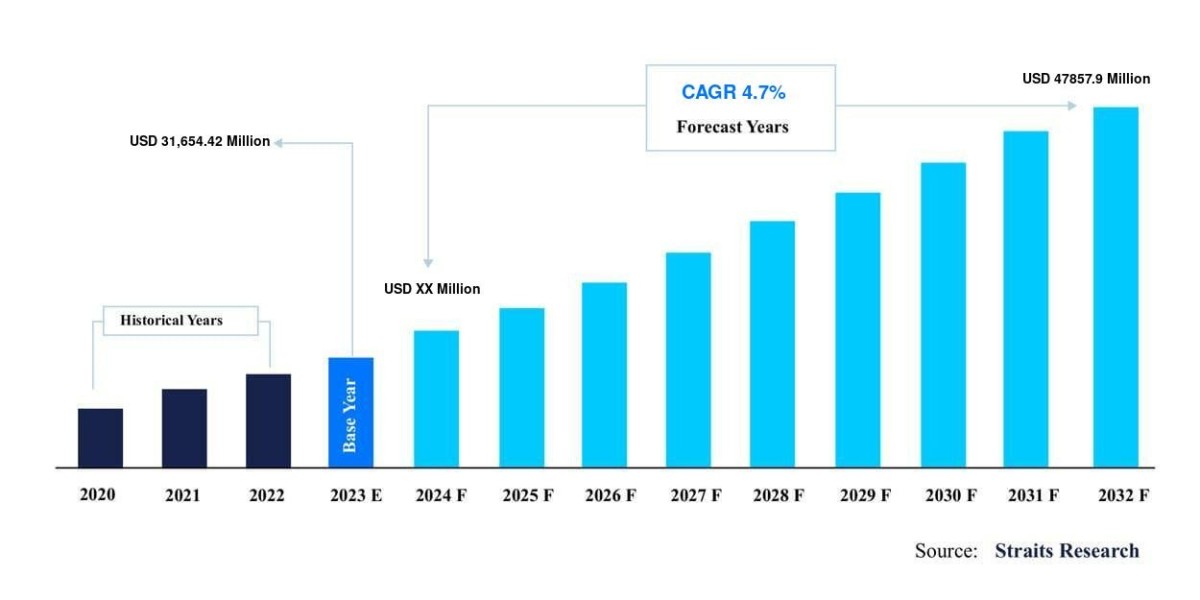
Buy the Full Report for More Regional Insights into the Bronchiectasis Clinical Trials