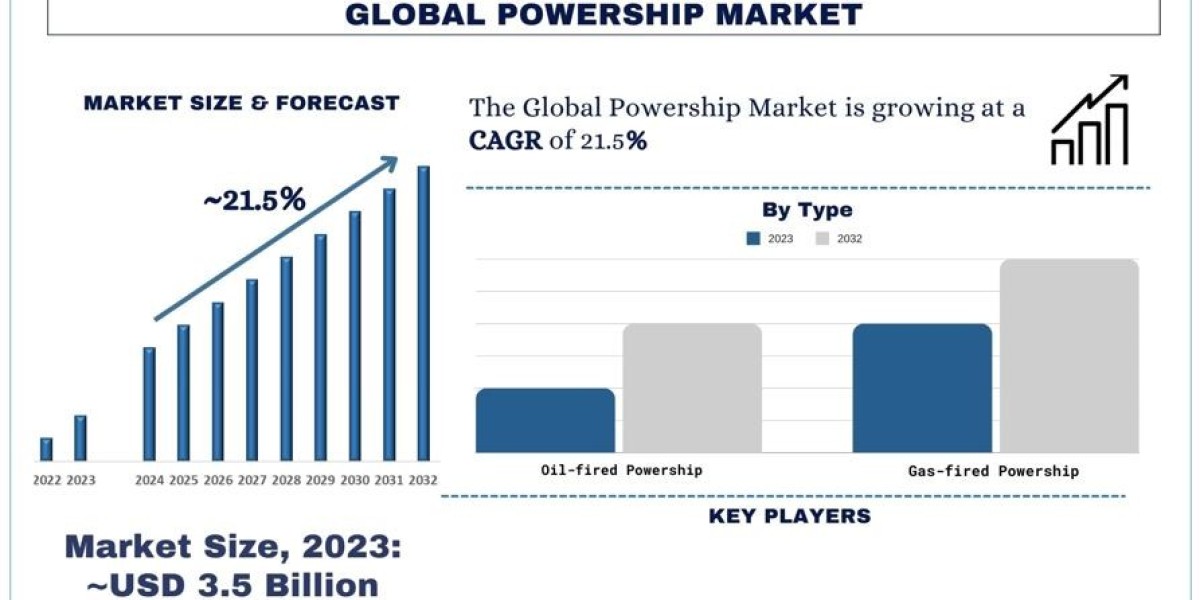
According to a new report by UnivDatos Market Insights, the Powership Market is expected to reach USD ~20 billion by 2032 by growing at a CAGR of ~21.5%. In this endeavour for recurrent and inconceivably stable energy generation practices, Powership has come to the forefront in tap for power generation around the globe. These mobile power plants based on oil-powered ships or oil barges provide instantaneous, manageable, and reliable power availability, which is most suitable for areas with constant power blackouts or less infrastructure development.
Access sample report (including graphs, charts, and figures): https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=63168&utm_source=LinkSJ&utm_medium=Snehal&utm_campaign=Snehal&utm_id=snehal
Demand:
The global demand for Powership is driven by a confluence of factors that underscore their strategic importance:
Emerging Economies: Industrialization and urbanization have resulted from population increases and increased demand for power in developing countries, which has resulted in an immense strain to the traditional power infrastructure. Powership helps to meet the need by expanding the supply circuit in a short time.
Emergency Power Needs: Disaster, political unrest, and infrastructure-related issues require conventional power management solutions. That is why it is possible to mention that Powership, being deployed rather quickly, is very helpful in such cases, bringing back power and stabilizing districts.
Infrastructure Limitations: In many remote or underdeveloped regions, building an ordinary power plant becomes either impossible or will take ages. Effectiveness—Powership makes an appropriate investment plan for providing electricity to regions that would otherwise receive minimal power supply.
Energy Transition: The coming-of-age of green energy, meaning that many nations are moving towards the utilization of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar, is where Powership comes in handy since it is an excellent balancing factor against the unpredictable nature of green energy.
For Instance:
Global electricity demand is expected to rise at a faster rate over the next three years, growing by an average of 3.4% annually through 2026. The gains will be driven by an improving economic outlook, which will contribute to faster electricity demand growth both in advanced and emerging economies. Particularly in advanced economies and China, electricity demand will be supported by the ongoing electrification of the residential and transport sectors, as well as a notable expansion of the data center sector. The share of electricity in final energy consumption is estimated to have reached 20% in 2023, up from 18% in 2015. While this is progress, electrification needs to accelerate rapidly to meet the world’s decarbonization targets. In the IEA’s Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario, a pathway aligned with limiting global warming to 1.5 °C, electricity’s share in final energy consumption nears 30% in 2030.
Applications:
Powerships are highly versatile, serving multiple applications across various sectors:
Emergency Power Supply: For emergency situations such as floods, hurricanes, and other natural disasters or lack of infrastructure support, Powership can swiftly be put into action. The fact that they can travel long distances makes it easier for them to get to areas where they are needed most, namely, to prepare electricity for aid operations.
Grid Support and Stabilization: Powerships play an important role in offsetting fluctuations in power grids by supplementing power during critical hours or when renewable energy resources are inauspicious. This makes the power supply to be constant at the needed volume without interrupted power failures or any temporary blackouts.
Industrial Power Supply: Industries located in remote areas or those requiring temporary power boosts during peak production times benefit greatly from Powership. They provide a reliable power source that can be adjusted based on the industrial demand.
Humanitarian Aid: They illuminate the areas affected by conflicts and disasters with electrical power for use in relief operations, refugee camps, and infrastructure. Being fully capable of delivering power as quickly and efficiently as possible is one of the reasons why they are so valued in humanitarian operations.
Cost
While Powership offers numerous advantages, it comes with significant costs that must be carefully managed:
Initial Investment: The construction and outfitting of a powership involve substantial capital expenditure. This includes the purchase or conversion of a ship, installation of power generation equipment, and specialized engineering work to ensure the vessel's efficiency and safety.
Operational Costs: Running a Powership involves ongoing expenses related to fuel, maintenance, and crew salaries. Fuel efficiency improvements and operational optimizations are crucial to managing these costs effectively.
Deployment Costs: Transporting Powership to their deployment sites and setting up connections to local power grids or networks add to the overall cost. These logistics must be planned meticulously to minimize delays and additional expenses.
Regulatory and Environmental Compliance: Meeting international regulations and addressing environmental concerns can also increase costs. Compliance with emission standards and obtaining necessary certifications require investments in technology and processes.
Click here to view the Report Description & TOC : https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=63168&utm_source=LinkSJ&utm_medium=Snehal&utm_campaign=Snehal&utm_id=snehal
Conclusion:
One factor that has unveiled the global Powership market for tremendous growth is the growing need for power solutions in many parts of the world that can only be met by flexible and quick deployment options. This means that the main drawbacks of Powership generating systems are high initial and operational costs; however, the benefits associated with rapid deployment, mobility, and flexibility of the system make this method most suitable for providing power supply in case of emergent shortages and supporting infrastructural developments.
The advanced features of fuel efficiency, hybrid power systems, and integration of renewable energy sources are expected to strengthen the sustainability of Powership and their affordability in the long run. When emerging economies transition from developing into developed ones, primarily where there is industrialization and urbanization, the demand for Powership is sure to increase, making them relevant players in the global power league.
In conclusion, through innovation that deserves flexibility and reliability, Powership unveils a perfect solution to the global power challenges as a dynamic market demand. The practicality with which they generate power and their efficiency in various situations makes them indispensable in the mission to ensure a steady, efficient, and sustainable flow of energy across the globe, hence achieving universal access to energy. It is clear, therefore, that ownership will remain a key player as the future energy market for power generation worldwide continues to shift.